Imagine a world where every electronic device around you is constantly battling against invisible waves of interference. Your smartphone might misbehave when you’re charging it, your laptop could glitch while you’re watching your favorite show, and your microwave might cause your Bluetooth speakers to emit annoying static. Sounds chaotic, right? Well, welcome to the world without EMI EMC filters!
What Does EMI EMC Stand For?
Before diving into the magic of EMI EMC filters, let’s decode the acronyms:
- EMI (Electromagnetic Interference): Think of this as the unwanted noise in the electronic symphony. It’s the disturbance that disrupts the normal operation of electronic devices.
- EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility): This is the harmonious balance ensuring that electronic devices operate as intended without causing or falling victim to EMI.
Brief Introduction to EMI EMC Filters
An EMI EMC filter is like the soundproofing in a concert hall, ensuring that the music (your devices) plays without unwanted background noise (interference). These filters are crucial components designed to suppress electromagnetic noise, ensuring that electronic equipment functions smoothly and coexists without causing electromagnetic chaos.
Whether it’s your household appliances, industrial machinery, or cutting-edge automotive electronics, EMI EMC filters play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and performance of these devices. They act as gatekeepers, allowing the desired signals to pass through while blocking out the pesky interference that could wreak havoc on device performance.
Importance of EMI EMC Filters in Electronic Devices
In our hyper-connected, gadget-driven world, the reliability and efficiency of electronic devices are paramount. Here’s why EMI EMC filters are indispensable:
- Enhanced Device Performance:
- By eliminating unwanted noise, these filters ensure that devices operate at their optimal capacity.
- Example: A computer with a high-quality EMI EMC filter will experience fewer crashes and glitches, providing a smoother user experience.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Many countries have strict regulations limiting the amount of electromagnetic noise devices can emit.
- Fact: Compliance with standards like FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in the USA or CE (Conformité Européenne) in Europe often mandates the use of EMI EMC filters.
- Protection of Sensitive Components:
- High-frequency interference can damage delicate electronic components over time.
- Case Study: In the automotive industry, EMI EMC filters protect critical systems like engine control units (ECUs) from electromagnetic disturbances, ensuring vehicle safety and reliability.
- Reduction of Electromagnetic Pollution:
- Minimizing EMI contributes to a cleaner electromagnetic environment, reducing the chances of interference between multiple devices operating simultaneously.
- Increased Longevity of Devices:
- By safeguarding electronics from constant interference, these filters help in prolonging the lifespan of devices, offering better return on investment for consumers and businesses alike.
Real-World Applications
To truly appreciate the significance of EMI EMC filters, consider their presence in everyday gadgets and complex machinery:
- Smartphones & Laptops: Ensuring clear signal transmission and preventing audio distortions.
- Medical Equipment: Vital in devices like MRI machines where precision is crucial.
- Industrial Machinery: Maintaining smooth operations in manufacturing plants by preventing electromagnetic disturbances.
- Automotive Systems: From infotainment units to safety systems, filters ensure reliable performance amidst the electromagnetic noise generated by vehicle operations.
EMI EMC filters are the silent warriors in the realm of electronics, tirelessly working behind the scenes to ensure that our devices communicate effectively, perform reliably, and coexist peacefully in an increasingly electromagnetic world.
What is EMI (Electromagnetic Interference)?
Imagine you’re trying to have a conversation in a bustling café. The background chatter, clinking of cups, and loud music can make it hard to hear your friend. In the electronics world, Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) is much like that background noise, but for electronic devices.
EMI Defined:
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) refers to the unwanted disturbances generated by external sources that affect the performance of electronic devices.
- These disturbances can be in the form of electromagnetic waves or noise that disrupt the normal operation of electronics.
Common Sources of EMI:
- Natural Sources:
- Lightning: Causes powerful electromagnetic pulses.
- Solar Flares: Emit high-energy particles affecting satellites and power grids.
- Man-Made Sources:
- Wireless Devices: Wi-Fi routers, cell phones, and Bluetooth devices.
- Household Appliances: Microwaves, refrigerators, and vacuum cleaners.
- Industrial Equipment: Motors, generators, and heavy machinery.
Types of EMI:
- Radiated EMI: Travels through the air as electromagnetic waves.
- Conducted EMI: Travels through power lines or other conductors.
Impact of EMI:
- Data Corruption: Leads to errors in data transmission, causing glitches in computers and smartphones.
- Device Malfunction: Causes unexpected behavior in electronic devices, such as resets or shutdowns.
- Reduced Performance: Slows down or limits the functionality of sensitive equipment like medical devices or communication systems.
Fun Fact: Did you know that the first documented case of EMI causing a problem was in the 1940s when radio broadcasts were disrupted by sparks from electrical circuits?
What is EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility)?
If EMI is the noise in our electronic café, then Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is all about ensuring that every device can not only withstand that noise but also play nicely with other devices without causing interference.
EMC Defined:
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electronic devices to operate as intended in their electromagnetic environment without causing or being susceptible to EMI.
- It ensures that devices coexist harmoniously, maintaining functionality and performance standards.
Key Aspects of EMC:
- Emission: How much electromagnetic noise a device generates.
- Immunity: How well a device can resist incoming electromagnetic noise without malfunctioning.
- Susceptibility: The degree to which a device can be affected by external electromagnetic disturbances.
Importance of EMC:
- Device Reliability: Ensures that devices function correctly in various environments, whether it’s a busy office or a quiet home.
- Safety: Prevents malfunctions in critical systems like medical equipment or automotive electronics that could lead to safety hazards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets international standards and regulations, allowing products to be sold globally without issues.
How EMC Relates to EMI EMC Filters:
- EMI EMC filters are designed to achieve EMC by minimizing the emission of electromagnetic noise from devices and enhancing their immunity to external interference.
- By integrating these filters, manufacturers can ensure their products meet EMC standards, leading to reliable and compliant electronic devices.
Real-World Example: Consider a modern car packed with electronic systems—navigation, entertainment, engine control units, and more. EMI EMC filters ensure that these systems operate without interfering with each other, providing a seamless and safe driving experience.
The Symbiotic Relationship Between EMI and EMC
To wrap things up, EMI and EMC are two sides of the same coin in the electronics universe:
- EMI is the disruptive force that can cause havoc in device performance.
- EMC is the harmonious balance that ensures devices operate smoothly despite potential interferences.
EMI EMC filters serve as the mediators in this relationship, filtering out the unwanted noise (EMI) and promoting compatibility (EMC) among electronic devices. Without these filters, our interconnected world of gadgets would be a cacophony of competing signals, leading to chaos and inefficiency.
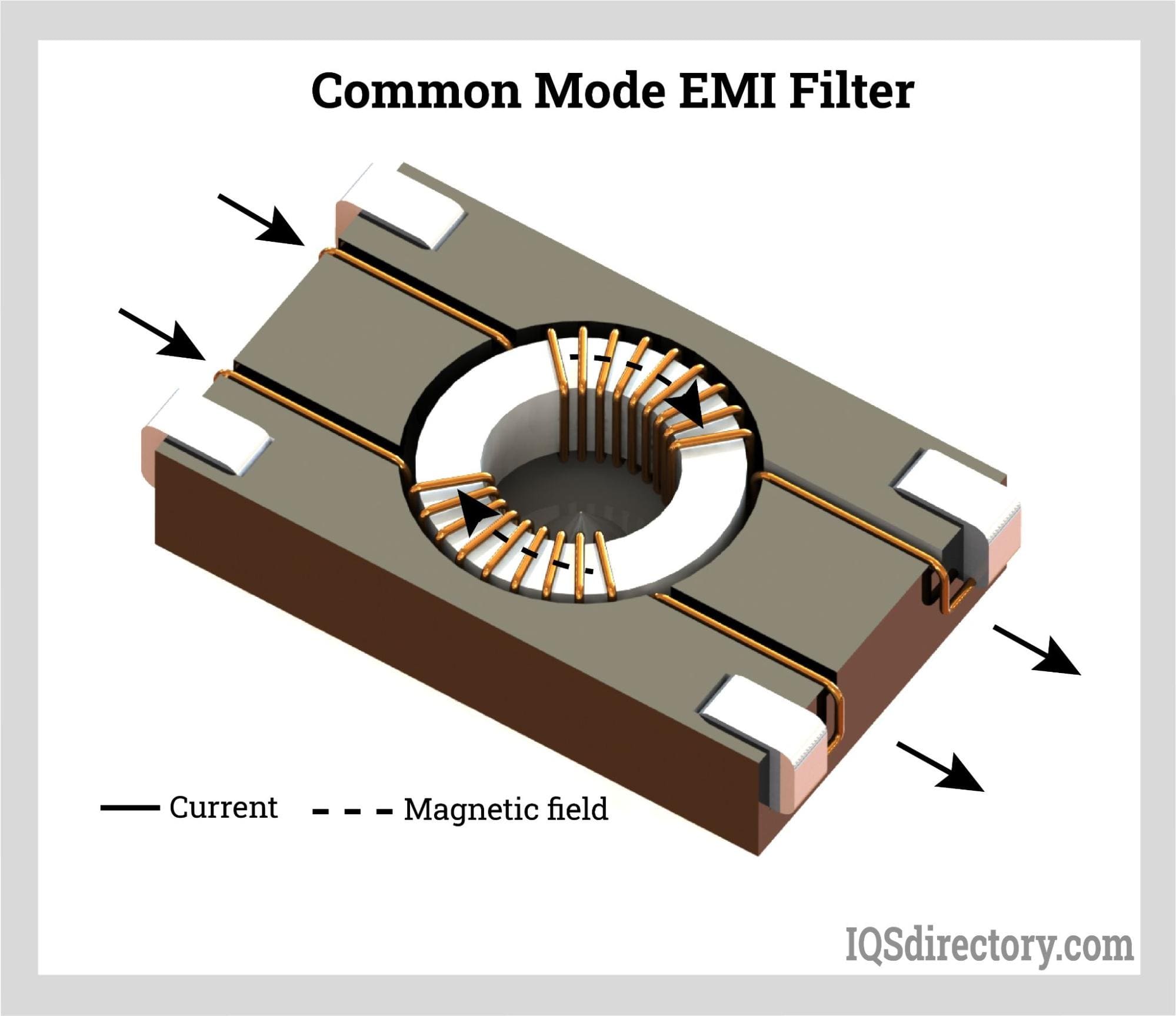
How Do EMI EMC Filters Work?
Now that we’ve unraveled the mysteries of EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) and EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility), it’s time to delve into the heart of the matter: How Do EMI EMC Filters Work? Think of these filters as the bouncers at a nightclub, meticulously checking every signal that enters and exits your electronic devices to ensure only the right “guests” get through. Let’s break down the magic behind these essential components.
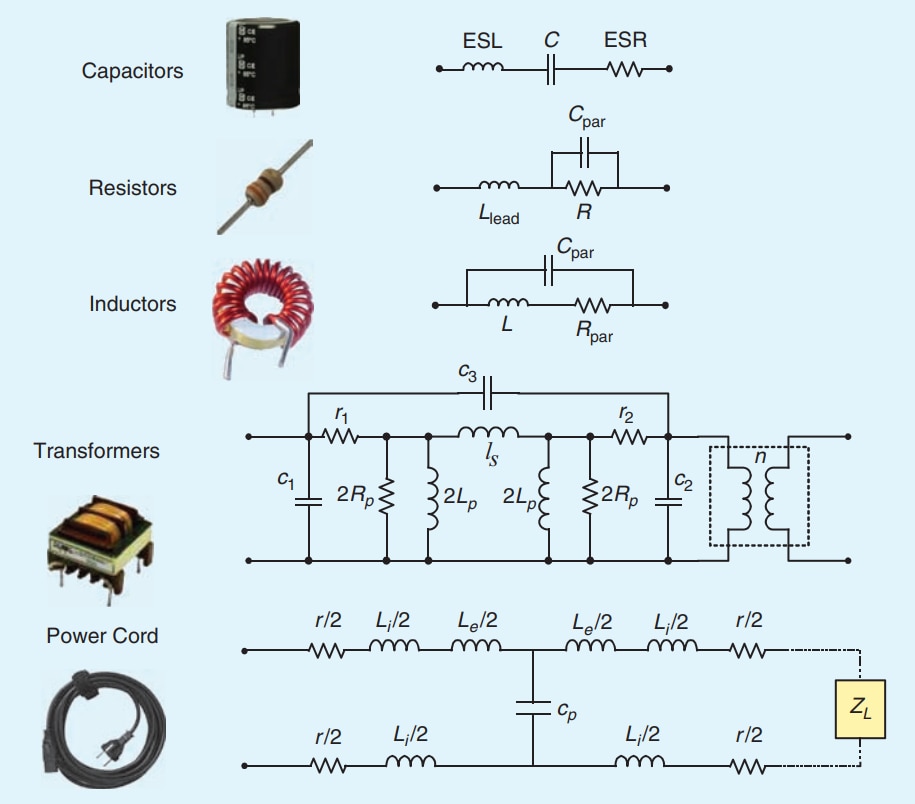
Components of an EMI EMC Filter
At the core of every EMI EMC filter are a few key players working in harmony to block unwanted interference while allowing your device to function seamlessly.
Inductors
- Role: Inductors are like the traffic cops of the filter world. They resist changes in current and are primarily responsible for blocking high-frequency noise.
- How They Work: When high-frequency electromagnetic waves try to pass through, inductors create a magnetic field that opposes the change, effectively reducing the noise.
Capacitors
- Role: Capacitors act as the gatekeepers, allowing only specific frequencies to pass through.
- How They Work: They store and release electrical energy, filtering out unwanted high-frequency signals by providing a low-impedance path to ground for these frequencies.
Resistors
- Role: Resistors help in dissipating any remaining noise that manages to sneak past the inductors and capacitors.
- How They Work: By providing resistance, they convert unwanted electrical energy into heat, further cleaning up the signal.
Ferrite Beads
- Role: These are the stealthy ninjas of the filter components, silently absorbing high-frequency noise without disturbing the desired signals.
- How They Work: Ferrite beads are made from ferromagnetic materials that absorb electromagnetic energy, effectively reducing noise across a broad frequency range.
Common Materials Used in EMI EMC Filters
- Ferrites: These ceramic compounds are essential for absorbing high-frequency noise.
- Metalized Films: Often used in capacitors, these films provide effective high-frequency filtering.
- Magnetic Cores: Inductors use magnetic cores made from materials like ferrite to enhance their ability to block interference.
Common Components of EMI EMC Filters
| Component | Function | Material |
|---|---|---|
| Inductors | Block high-frequency noise | Magnetic cores (ferrite) |
| Capacitors | Allow specific frequencies to pass | Metalized films |
| Resistors | Dissipate residual noise | Carbon, metal film |
| Ferrite Beads | Absorb a wide range of high-frequency noise | Ferrite materials |
The Filtering Process Explained
Understanding how EMI EMC filters work requires a look at the journey of an electrical signal through these components. Let’s break it down step-by-step.
1. Signal Entry
When an electrical signal enters a device, it carries both the desired information (like data or power) and unwanted electromagnetic noise (EMI).
2. Inductive Filtering
- Inductors resist rapid changes in current, effectively blocking high-frequency noise from passing through.
- They allow the steady, low-frequency power signals to continue unhindered, ensuring your device receives the power it needs without interruption.
3. Capacitive Filtering
- Capacitors provide a path for high-frequency noise to be diverted away from the main signal path.
- By shunting these unwanted frequencies to the ground, capacitors prevent them from reaching sensitive components within the device.
4. Dissipation of Residual Noise
- Resistors and ferrite beads come into play to handle any remaining noise that wasn’t blocked by inductors and capacitors.
- Resistors convert this residual noise into heat, while ferrite beads absorb and dissipate it, ensuring the signal that reaches your device is as clean as possible.
5. Signal Output
The result is a purified electrical signal that maintains the integrity of your device’s operation, free from the disruptive effects of EMI.
Difference Between Common-Mode and Differential-Mode Filtering
Understanding the types of interference is crucial for grasping how filters tackle them:
Common-Mode Interference
- Definition: Noise that appears equally and in-phase on both the signal and return paths.
- Filtering Approach: Common-mode filters are designed to suppress this type of noise by providing a high impedance path for the interference while allowing the desired signal to pass through unaffected.
Differential-Mode Interference
- Definition: Noise that appears between the signal and return paths, often caused by unbalanced disturbances.
- Filtering Approach: Differential-mode filters specifically target and attenuate these disturbances without impacting the desired signal.
Types of EMI EMC Filters
Not all EMI EMC filters are created equal. Depending on the application and specific requirements, different types of filters are employed to tackle various forms of interference.
Power Line Filters
- Purpose: Designed to clean the power supply lines, ensuring that devices receive steady and noise-free power.
- Applications: Commonly used in computers, TVs, and other household electronics to prevent power-related EMI from affecting device performance.
Signal Line Filters
- Purpose: Focus on filtering noise from signal transmission lines, ensuring that data and communication signals remain clear.
- Applications: Essential in telecommunications, networking equipment, and audio/video systems where signal integrity is paramount.
Specialized Filters for Different Applications
- Automotive Filters: Tailored to withstand the harsh electrical environments of vehicles, protecting critical systems from electromagnetic disturbances.
- Medical Device Filters: Ensure that sensitive medical equipment operates reliably without interference, which is crucial for patient safety.
- Industrial Filters: Robust filters used in manufacturing and heavy machinery to maintain smooth operations in electrically noisy environments.
List: Common Types of EMI EMC Filters
- Power Line Filters
- Clean power supplies
- Prevent power-related EMI
- Signal Line Filters
- Maintain data integrity
- Essential for communication systems
- Automotive Filters
- Protect vehicle electronics
- Withstand harsh electrical conditions
- Medical Device Filters
- Ensure reliable operation of medical equipment
- Enhance patient safety
- Industrial Filters
- Maintain smooth operations in manufacturing
- Reduce electromagnetic disturbances in heavy machinery
Case Study: EMI EMC Filters in Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a prime example of where EMI EMC filters play a critical role. With numerous electronic systems operating simultaneously—from battery management to infotainment and safety features—EVs are susceptible to a myriad of electromagnetic interferences.
Scenario: An electric car without adequate EMI EMC filtering experiences interference between the battery management system and the infotainment unit. This results in erratic behavior like sudden reboots of the entertainment system and inaccurate battery readings, potentially compromising both user experience and vehicle safety.
Solution: By integrating high-quality EMI EMC filters into the power and signal lines of the EV’s electronic systems, manufacturers can effectively block the unwanted noise. This ensures that each system operates smoothly without interfering with one another, enhancing both the reliability and safety of the vehicle.
Outcome: The implementation of EMI EMC filters leads to:
- Stable Performance: Infotainment systems operate without interruptions.
- Accurate Readings: Battery management systems provide precise information, crucial for vehicle efficiency.
- Enhanced Safety: Critical safety features remain unaffected by electromagnetic disturbances.
This case study underscores the indispensable role of EMI EMC filters in complex, high-stakes applications like electric vehicles, where reliability and safety are non-negotiable.
Understanding how EMI EMC filters work provides valuable insights into their indispensable role in modern electronics. By leveraging components like inductors, capacitors, resistors, and ferrite beads, these filters effectively cleanse electrical signals of unwanted noise. Whether it’s maintaining the performance of your smartphone, ensuring the safety of medical equipment, or powering the next generation of electric vehicles, EMI EMC filters are the unsung heroes that keep our electronic world running smoothly.

Applications of EMI EMC Filters
Now that we’ve explored what EMI EMC filters are and how they work, let’s dive into the exciting world of where these filters make their mark. From the gadgets in your pocket to the massive machinery in factories, EMI EMC filters play a crucial role in ensuring everything operates smoothly and without interference. Buckle up as we journey through the diverse applications of these unsung heroes of the electronics world!
Consumer Electronics
In our daily lives, consumer electronics are everywhere—from the smartphones we can’t live without to the refrigerators that keep our veggies fresh. EMI EMC filters ensure these devices function seamlessly by preventing electromagnetic noise from causing glitches or performance issues.
- Smartphones & Tablets:
- Functionality: Filters maintain clear signal transmission, ensuring your calls don’t drop and your data stays intact.
- Example: Without EMI EMC filters, your phone might experience unexpected shutdowns or slow down when charging.
- Laptops & Computers:
- Performance: Keeps your system running smoothly by reducing data corruption and preventing crashes caused by electromagnetic interference.
- Fun Fact: Ever noticed how some laptops heat up more than others? Quality EMI EMC filters can help manage power distribution, indirectly affecting device temperature.
- Home Appliances:
- Reliability: Appliances like microwaves, washing machines, and smart TVs rely on filters to prevent interference that could disrupt their operations.
- Case Study: A smart refrigerator with integrated EMI EMC filters ensures that its internal sensors communicate effectively with your smartphone, providing real-time updates without interference.
Industrial Equipment
In the bustling environment of industrial settings, machinery and equipment are often subjected to harsh electromagnetic conditions. EMI EMC filters are indispensable in these scenarios, safeguarding both the equipment and the data they handle.
- Manufacturing Machines:
- Operation: Filters prevent electromagnetic noise from disrupting the precision of automated machinery, ensuring consistent production quality.
- Impact: Reduces downtime caused by equipment malfunctions, leading to increased productivity and lower maintenance costs.
- Power Supplies & Transformers:
- Stability: Ensures that power distribution remains stable by filtering out noise that could cause fluctuations or damage sensitive components.
- Example: In a factory setting, stable power means fewer interruptions in the assembly line, keeping everything running like a well-oiled machine.
- Robotics:
- Precision: Critical for the accurate movement and operation of industrial robots, filters prevent interference that could lead to errors or accidents.
- Safety: Enhances the safety of automated processes by ensuring robots respond correctly to control signals without unexpected disruptions.
Automotive Industry
Modern vehicles are marvels of technology, packed with electronic systems that enhance performance, safety, and comfort. EMI EMC filters are essential in the automotive industry to ensure all these systems work harmoniously without interfering with each other.
- Engine Control Units (ECUs):
- Function: Filters protect ECUs from electromagnetic disturbances, ensuring accurate engine performance and efficient fuel usage.
- Benefit: Enhanced engine reliability and reduced emissions, contributing to a smoother and more environmentally friendly drive.
- Infotainment Systems:
- Entertainment: Keeps audio and video systems free from interference, providing a seamless entertainment experience without static or signal loss.
- Connectivity: Ensures that features like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi operate without disruptions, maintaining strong connections for navigation and streaming.
- Safety Systems:
- Reliability: Critical safety features such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS), airbags, and electronic stability control rely on filters to function correctly.
- Impact: Prevents malfunctions that could compromise vehicle safety, ensuring that safety systems activate precisely when needed.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Battery Management: Filters play a pivotal role in managing the complex interactions between battery systems and electronic controls, ensuring efficient energy usage and longevity.
- Charging Systems: Ensures that charging stations deliver clean power, preventing interference that could affect the vehicle’s electronic systems.
Telecommunications
In the age of instant communication, maintaining the integrity of data transmission is paramount. EMI EMC filters are the unsung heroes in the telecommunications sector, ensuring that information flows smoothly without electromagnetic hiccups.
- Networking Equipment:
- Data Integrity: Filters prevent electromagnetic noise from causing data loss or corruption in routers, switches, and servers.
- Performance: Ensures high-speed data transfer without interruptions, supporting the backbone of the internet and corporate networks.
- Cell Towers & Base Stations:
- Signal Clarity: Maintains clear and consistent communication signals by filtering out interference from various sources.
- Reliability: Reduces the chances of dropped calls and weak signals, enhancing overall communication reliability.
- Fiber Optic Systems:
- Protection: Although fiber optics are less susceptible to EMI, the associated electronic equipment still relies on EMI EMC filters to maintain signal quality.
- Efficiency: Ensures that data transmitted over long distances remains intact and free from electromagnetic disturbances.
- Broadcasting Equipment:
- Quality: Filters help maintain high-quality audio and video broadcasts by preventing electromagnetic noise from degrading the signal.
- Reach: Ensures that broadcast signals reach their intended audience without interference, maintaining the integrity of live events and broadcasts.
Medical Equipment
In the medical field, precision and reliability are non-negotiable. EMI EMC filters are critical in ensuring that medical devices operate without interference, safeguarding both patients and healthcare providers.
- Diagnostic Machines:
- Accuracy: Devices like MRI machines, X-rays, and CT scanners rely on filters to maintain signal integrity, ensuring accurate diagnostics.
- Safety: Prevents electromagnetic interference that could lead to incorrect readings or malfunctioning of critical diagnostic tools.
- Life-Support Systems:
- Reliability: Filters ensure that life-support devices such as ventilators and heart monitors operate without disruption, maintaining patient safety.
- Consistency: Provides a stable and interference-free environment for sensitive medical equipment, crucial for patient care.
- Wearable Medical Devices:
- Functionality: Ensures that devices like insulin pumps and pacemakers communicate effectively without electromagnetic disturbances.
- Patient Comfort: Reduces the risk of device malfunctions, enhancing the reliability and trust in wearable medical technology.
- Hospital Infrastructure:
- Network Systems: Filters help maintain the integrity of hospital network systems, ensuring that patient data is transmitted accurately and securely.
- Communication Systems: Ensures that communication devices within the hospital operate without interference, facilitating effective coordination among healthcare teams.
Telecommunications Infrastructure
In the realm of telecommunications infrastructure, maintaining clear and uninterrupted data flow is essential. EMI EMC filters ensure that the backbone of our communication networks remains robust and reliable.
- Data Centers:
- Operation: Filters maintain the integrity of power supplies and data transmission lines, preventing electromagnetic noise from disrupting server operations.
- Efficiency: Enhances the performance of data centers by reducing the likelihood of hardware failures and data corruption caused by EMI.
- Satellite Communications:
- Signal Quality: Ensures that signals transmitted and received by satellites remain clear and free from electromagnetic interference.
- Reliability: Critical for maintaining consistent communication links between ground stations and satellites, essential for global connectivity.
- Wireless Networks:
- Coverage: Filters help maintain strong and reliable wireless signals, ensuring that users experience minimal interference and maximum coverage.
- Performance: Reduces latency and improves data throughput by minimizing electromagnetic disturbances in wireless transmission.
Renewable Energy Systems
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, the integration of electronic systems in solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage solutions necessitates the use of EMI EMC filters to ensure efficient and reliable operation.
- Solar Power Inverters:
- Efficiency: Filters help maintain clean power conversion, reducing losses caused by electromagnetic interference.
- Longevity: Protects inverters from damage caused by high-frequency noise, extending their operational lifespan.
- Wind Turbines:
- Control Systems: Ensures that control electronics operate without interference, maintaining optimal turbine performance.
- Data Transmission: Filters facilitate accurate data transmission from turbines to monitoring systems, aiding in efficient energy management.
- Energy Storage Systems:
- Battery Management: Filters ensure that energy storage systems communicate effectively with power grids, preventing electromagnetic disturbances that could affect energy distribution.
- Safety: Protects storage systems from electrical noise that could lead to malfunctions or safety hazards.
Aerospace and Defense
In the high-stakes world of aerospace and defense, the reliability of electronic systems can mean the difference between mission success and failure. EMI EMC filters are vital in ensuring that these systems operate flawlessly under demanding conditions.
- Aircraft Avionics:
- Navigation Systems: Filters maintain the accuracy of GPS and other navigation tools by preventing electromagnetic interference.
- Communication Systems: Ensures clear and uninterrupted communication between pilots and ground control, critical for flight safety.
- Military Equipment:
- Radars and Communication Gear: Filters help maintain the clarity and reliability of radar systems and communication devices, essential for tactical operations.
- Weapon Systems: Ensures that electronic weapon systems operate without interference, maintaining their effectiveness and reliability.
- Satellites and Spacecraft:
- Signal Integrity: Filters maintain the integrity of communication signals between spacecraft and ground stations, ensuring successful missions.
- System Reliability: Protects sensitive electronic components from electromagnetic disturbances in the harsh environment of space.
Key Applications of EMI EMC Filters
| Application Area | Usage of EMI EMC Filters | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones, laptops, home appliances | Enhanced performance, reduced glitches |
| Industrial Equipment | Manufacturing machines, power supplies, robotics | Increased productivity, equipment reliability |
| Automotive Industry | ECUs, infotainment systems, safety features, EVs | Improved vehicle performance and safety |
| Telecommunications | Networking equipment, cell towers, fiber optics, broadcasting | Clear signal transmission, reliable communication |
| Medical Equipment | Diagnostic machines, life-support systems, wearable devices | Accurate diagnostics, patient safety |
| Renewable Energy | Solar inverters, wind turbines, energy storage systems | Efficient energy conversion, system longevity |
| Aerospace and Defense | Avionics, military equipment, satellites | Mission reliability, effective operations |
Real-World Example: EMI EMC Filters in Smart Homes
Imagine a modern smart home filled with interconnected devices: smart thermostats, security cameras, smart lights, and voice-activated assistants. Each of these gadgets communicates wirelessly, creating a convenient and efficient living environment. However, with so many devices operating simultaneously, the potential for electromagnetic interference is high.
Scenario: A smart thermostat in your home is experiencing connectivity issues, causing it to malfunction and leading to inconsistent temperature control. This not only affects comfort but also increases energy consumption and costs.
Solution: By integrating EMI EMC filters into the power lines and communication pathways of the smart thermostat and other connected devices, the interference is significantly reduced. The filters ensure that the thermostat communicates clearly with your smartphone and other smart home hubs without disruptions.
Outcome:
- Consistent Performance: The smart thermostat operates reliably, maintaining the desired temperature without unexpected shutdowns.
- Energy Efficiency: Improved communication between devices leads to better energy management, reducing utility bills.
- Enhanced User Experience: Users enjoy a seamless and frustration-free smart home environment, encouraging further adoption of connected technologies.
This example highlights how EMI EMC filters are essential in creating efficient and reliable smart home ecosystems, ensuring that the convenience of connected devices doesn’t come at the cost of performance and reliability.
From the gadgets we use every day to the sophisticated systems that drive industries and safeguard our safety, EMI EMC filters are integral to the smooth and reliable operation of electronic devices and systems. By mitigating electromagnetic interference and promoting electromagnetic compatibility, these filters ensure that our modern world remains interconnected and efficient. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an industry professional, or simply a curious mind, understanding the applications of EMI EMC filters underscores their vital role in the tapestry of modern technology.