What is RFI Interference?
Imagine you’re watching your favorite TV show, and suddenly, the screen fills with static. Or worse, your Wi-Fi drops just as you’re about to win an online game. That, my friends, is Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) at work. RFI happens when unwanted radio signals disrupt the functioning of electronic devices. It’s like that one party crasher who ruins the vibe—except this guest messes with your gadgets instead of your playlist.
Why is RFI Interference a Problem?
RFI isn’t just an inconvenience; it can have serious consequences. Businesses can lose productivity due to malfunctioning equipment. Hospitals might face life-threatening risks if their sensitive medical devices are compromised. And at home, interference might turn a simple video call into a frustrating game of “Can you hear me now?”
Why You Should Care About RFI Interference
Addressing RFI interference improves device reliability, boosts signal strength, and ensures compliance with industry standards. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a professional dealing with critical systems, or just a frustrated homeowner, understanding and mitigating RFI interference can make your life smoother and less static-filled.

What Causes RFI Interference?
At its core, RFI interference is like a bad neighbor: it doesn’t respect boundaries. It’s caused by unwanted electromagnetic signals bleeding into areas they shouldn’t. Here’s a breakdown of the usual suspects:
- Electromagnetic Radiation from Devices
Modern life is full of gadgets, and many of them emit electromagnetic waves—whether it’s your microwave oven humming away, your smartphone constantly checking for notifications, or your Wi-Fi router broadcasting internet magic. - Natural Phenomena
Did you know that nature also contributes to RFI? Lightning strikes, solar flares, and even auroras can generate interference that disrupts radio signals. Thankfully, you can’t blame Mother Nature for most of your Wi-Fi woes (though that would be convenient). - Man-Made Sources
- Power lines can emit electrical noise.
- Industrial machinery often generates interference.
- Wireless devices, like Bluetooth headsets or baby monitors, can also wreak havoc when they’re too close to sensitive equipment.
Types of RFI Interference
Understanding the different types of RFI is key to tackling the problem. Let’s break them down:
- Conducted RFI
This type travels along electrical wiring and cabling. It’s like that one overly chatty friend who can’t stop calling. If your device shares wiring with the interference source, the signals might come through loud and clear—literally. - Radiated RFI
Here, the interference is transmitted through the air as electromagnetic waves. Think of it as Wi-Fi signals gone rogue, crossing paths with devices that aren’t designed to handle them. - Narrowband vs. Broadband Interference
- Narrowband interference: Targets specific frequencies, like the static interrupting your favorite FM radio station.
- Broadband interference: Covers a wide range of frequencies, often creating a more pervasive nuisance.
How RFI Affects Devices
RFI interference doesn’t discriminate. It can throw a wrench into everything from your household electronics to critical industrial systems:
- Communication Systems: Expect poor audio quality, dropped calls, or loss of signal clarity on radios, TVs, or cell phones.
- Medical Equipment: Pacemakers, MRI scanners, and other devices are highly sensitive to RFI, making it a literal matter of life and death.
- Industrial and Commercial Equipment: Control systems, alarms, and even power grids can experience malfunctions. Remember the Northeast blackout of 2003? While not solely due to RFI, similar disruptions can escalate quickly.
A Real-World Example
In 2021, a small British village lost its internet connection every morning. The culprit? An old TV emitting interference at the same time each day. The solution? Convincing the owner to retire their beloved relic. Sometimes, solving RFI interference is equal parts science and detective work!

How to Detect RFI Interference
Signs of RFI Interference
Detecting RFI interference can feel like hunting for a needle in a haystack—especially when it manifests in subtle or intermittent ways. Here are some tell-tale signs to watch for:
- Static or Noise in Communication Systems
- Crackling sounds on radios or distorted audio on phone calls.
- Poor video or audio quality in TV broadcasts.
- Erratic Device Behavior
- Wi-Fi signals dropping unpredictably.
- Random glitches in home automation systems or smart devices.
- Signal Degradation or Loss
- Weak or intermittent signals in wireless networks.
- Reduced performance in Bluetooth connections or GPS systems.
If any of these issues sound familiar, it’s time to roll up your sleeves and investigate further.
Tools for Identifying RFI
Thankfully, modern technology offers plenty of gadgets to help pinpoint the source of interference. Here’s a toolkit to get you started:
- Spectrum Analyzers
- These devices allow you to visualize and analyze the frequency spectrum.
- Ideal for identifying specific bands affected by interference.
- Directional Antennas
- Help you locate the source of radiated RFI by focusing on specific areas.
- Great for narrowing down outdoor or large-scale interference sources.
- Portable Receivers and Sniffers
- Handheld devices that detect and trace interference signals.
- Compact and user-friendly for quick diagnostics.
Steps to Perform a Site Survey
A site survey is like playing detective—collecting clues, analyzing patterns, and solving the mystery of RFI. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Prepare Your Equipment
- Gather tools such as a spectrum analyzer, portable receiver, and directional antenna.
- Ensure devices are charged and calibrated for accurate readings.
- Identify Affected Frequencies
- Use a spectrum analyzer to scan for unusual peaks or disruptions in the frequency bands your devices use.
- Note which frequencies are consistently experiencing interference.
- Map Interference Sources
- Walk through the area with your tools, noting signal strength changes.
- Pay close attention to proximity to potential culprits like routers, power lines, or large metal structures.
- Document Findings
- Take detailed notes on locations, signal strength, and the time of day when interference occurs.
- Use this data to build a complete picture of the interference problem.
Pro Tip: Interference can fluctuate depending on external factors, such as time of day or nearby activity. Be sure to conduct surveys at multiple times for a comprehensive analysis.
Common Challenges in Detecting RFI
Even with the right tools, detecting RFI can be tricky. Here are some obstacles and how to overcome them:
- Multiple Sources: Interference might stem from more than one source. Solution? Address each source individually, starting with the most disruptive.
- Intermittent Interference: Fluctuations can make it hard to pinpoint the source. Tip? Keep a log of when issues occur to identify patterns.
- False Positives: Some devices might mimic interference. Verify findings by switching off suspected sources and observing changes.
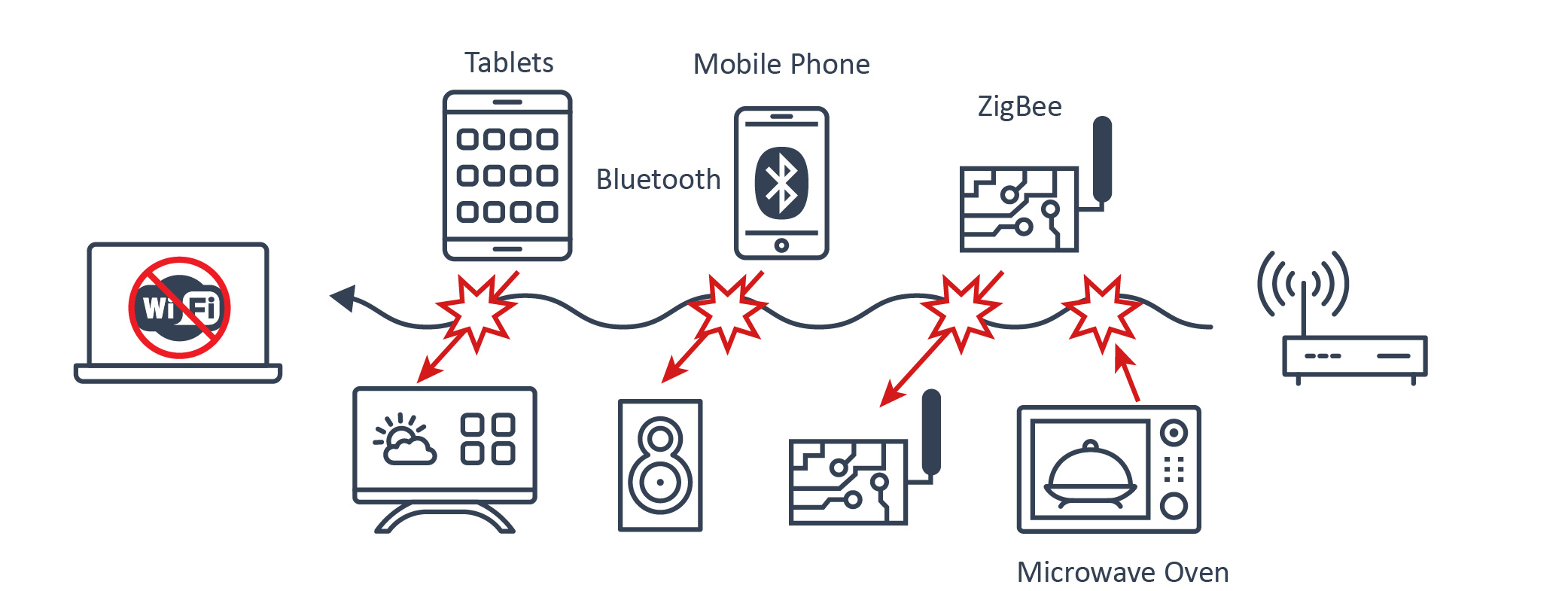
How to Stop RFI Interference
Immediate Solutions
When dealing with RFI interference, quick fixes can often resolve the issue or at least reduce its impact. Here are a few practical steps you can take right away:
- Turn Off or Relocate Devices
- Identify any electronic devices near your affected equipment. Switch them off or move them farther apart.
- Example: If your Wi-Fi signal is dropping due to a nearby cordless phone, moving the router to a different room can help.
- Re-route Cables
- Avoid running power and signal cables parallel to each other. Instead, cross them at right angles to minimize interference.
- Bonus Tip: Use shorter cables whenever possible to reduce susceptibility to conducted RFI.
- Adjust Device Placement
- Maintain a healthy distance between devices that emit strong electromagnetic signals, such as microwaves, and sensitive electronics like modems or TVs.
Shielding Techniques
Shielding is like giving your devices a protective suit of armor. Here’s how you can fortify them:
- Use Shielded Cables and Connectors
- Replace regular cables with shielded variants, which have a protective layer to block external interference.
- Ensure connectors are well-fitted and don’t leave gaps where RFI can sneak in.
- Install Faraday Cages
- For critical equipment, use Faraday cages—enclosures made of conductive material that block electromagnetic signals.
- Fun Fact: Even your microwave oven works like a mini Faraday cage to keep radiation inside!
- Proper Grounding
- Grounding eliminates unwanted signals by providing a safe path for excess electromagnetic energy.
- Always follow local electrical codes to ensure proper installation.
Filtering and Suppression
Filtering and suppressing RFI is like adding a bouncer to your signal party—only the right frequencies get in.
- Low-Pass and High-Pass Filters
- Low-pass filters block high-frequency interference, while high-pass filters keep low-frequency signals at bay.
- Choose the type of filter based on the frequencies causing problems.
- Ferrite Cores
- Clip-on ferrite cores are inexpensive and easy to install on cables. They reduce high-frequency noise and are especially useful for power cords.
- Pro Tip: Add ferrite cores to both ends of a cable for maximum suppression.
- Noise Suppressors and Isolators
- Use inline suppressors to filter out unwanted signals from power lines.
- Isolators can decouple devices, preventing interference from spreading.
Software-Based Solutions
Technology isn’t just the problem—it can also be the solution.
- Frequency Adjustments
- Adjust the operating frequencies of your devices to avoid overlapping with interference sources. For example, switch your Wi-Fi from the crowded 2.4 GHz band to the less congested 5 GHz band.
- Firmware Updates
- Manufacturers often release firmware updates to improve a device’s resistance to interference. Check for updates regularly!
- Channel Optimization
- For routers and wireless devices, use built-in tools or apps to find the least congested channel.
Case Study: Shielding Success
In a hospital setting, life-support monitors were experiencing disruptions due to interference from a nearby industrial plant. By installing shielded cables, adding ferrite cores, and grounding the equipment, technicians eliminated the interference and restored reliable operation. The lesson? Small changes can make a big difference.
Long-Term Strategies to Prevent RFI Interference
Design Considerations for New Installations
The best way to tackle RFI interference is to stop it before it starts. Thoughtful planning during equipment installation can save you headaches down the line.
- Choose RFI-Resistant Equipment
- Look for devices labeled as EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) compliant. These are designed to coexist with other electronic devices without causing or being affected by interference.
- Check for certifications like FCC compliance in the U.S. or CE marking in Europe.
- Strategic Layout and Grounding
- Place sensitive devices (e.g., communication equipment) away from potential sources of interference like heavy machinery or electrical panels.
- Use a star grounding system, where all grounding paths connect to a central point, to minimize interference loops.
- Cable Management Best Practices
- Use twisted-pair cabling for Ethernet connections to cancel out electromagnetic noise.
- Bundle cables neatly and avoid tangled or unprotected wires, which can act as antennas for RFI.
Compliance with Regulations
Regulatory standards exist for a reason: they help prevent interference chaos. Staying compliant not only reduces interference but also protects you legally.
- FCC and CE Standards
- The FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in the U.S. and the CE (Conformité Européenne) mark in Europe set limits for electromagnetic emissions.
- Ensure all devices meet these standards before installation.
- Testing and Certification
- Conduct EMI/RFI testing during product development to ensure compliance.
- Certifications provide peace of mind that your equipment won’t cause or fall victim to interference.
- Industry-Specific Regulations
- Some sectors, such as aviation or healthcare, have stricter rules due to the critical nature of their operations. Always consult sector-specific guidelines.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Even the best installations can degrade over time. Routine checks can nip potential interference problems in the bud.
- Scheduled Equipment Inspections
- Regularly inspect cables, connectors, and grounding systems for wear and tear.
- Replace aging or damaged components promptly.
- Periodic Interference Scans
- Conduct site surveys every few months to detect new interference sources.
- Use tools like spectrum analyzers to ensure signals remain clean and within safe limits.
- Firmware and Software Updates
- Many manufacturers release updates to enhance device performance and mitigate interference vulnerabilities. Stay up-to-date!
Case Study: Preventive Design in Action
A tech startup faced repeated Wi-Fi dropouts in their office due to interference from nearby industrial equipment. By implementing shielded Ethernet cables, installing a star grounding system, and investing in FCC-certified routers, they not only resolved the issue but also future-proofed their network.
Pro Tip for Prevention: Keep an interference log! Track when and where issues occur, even if they seem minor. Over time, this can help you spot patterns and address potential threats before they escalate.