Have you ever been in the middle of an important Zoom meeting only to have your screen freeze or your audio cut out unexpectedly? Or perhaps you’ve noticed your Wi-Fi signal dropping just when you need it most? Chances are, Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) noise is the culprit behind these frustrating tech hiccups. EMI noise refers to unwanted disturbances that affect electrical circuits and devices, disrupting their normal operation. This interference can originate from a myriad of sources, both common and unexpected. Think household electronics like microwaves and cordless phones, industrial machinery humming in the background, automotive electronics in your car, or even your trusty smartphone and laptop. These everyday gadgets emit electromagnetic waves that, when not properly managed, can create a cacophony of interference, leading to degraded performance or complete malfunction of your devices.
Importance of Addressing EMI Noise
Why should you care about EMI noise? Well, aside from the obvious annoyance of having your devices act up, EMI noise can have significant repercussions on both device performance and personal well-being. For starters, EMI can severely impact the functionality of your electronics. Imagine trying to stream your favorite show only to have it constantly buffer, or attempting to charge your phone while experiencing interference that slows down the process. In more critical environments, such as hospitals or industrial settings, EMI noise can interfere with sensitive equipment, posing health and safety risks. Additionally, persistent EMI issues can lead to increased energy consumption as devices struggle to operate efficiently, ultimately shortening their lifespan and leading to higher maintenance costs.

To effectively stop EMI noise, it’s crucial to first grasp what EMI noise is and how it impacts your devices and environment.
What is EMI Noise?
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) noise is like that uninvited guest at a party who just won’t leave, causing chaos and disrupting the flow. In technical terms, EMI noise refers to unwanted electromagnetic energy that disrupts the normal operation of electronic devices. This interference can be radiated or conducted, meaning it can travel through the air or along electrical conductors, respectively.
Types of EMI Noise:
- Radiated EMI:
- Travels through the air as electromagnetic waves.
- Common sources include wireless devices, radio transmitters, and even natural phenomena like lightning.
- Conducted EMI:
- Travels along electrical conductors such as power lines or cables.
- Often originates from power supplies, motors, and faulty wiring.
Understanding these types helps in pinpointing where the interference is coming from and how to tackle it effectively.
Common Sources of EMI Noise
EMI noise is ubiquitous in our modern world, thanks to the proliferation of electronic devices. Here are some of the most common culprits:
- Household Electronics:
- Wi-Fi Routers: Constantly emitting radio waves can interfere with other wireless devices.
- Microwaves: Their operation can disrupt nearby electronics, especially Wi-Fi signals.
- LED Lights: Poorly designed LEDs can emit EMI that affects other devices.
- Industrial Equipment:
- Machinery and Motors: Large industrial machines can generate significant EMI.
- Welding Equipment: Sparks and electrical arcs are notorious for creating interference.
- Automotive Electronics:
- Engine Control Units (ECUs): These can emit EMI that affects other car electronics.
- Audio Systems: High-powered car stereos can interfere with navigation and communication systems.
- Personal Devices:
- Smartphones and Laptops: Constant connectivity and wireless communication make them sources of EMI.
- Bluetooth Devices: Headphones and speakers can introduce interference, especially in densely packed device environments.
- External Sources:
- Radio Towers: Nearby radio and TV towers can emit powerful electromagnetic waves.
- Power Lines: High-voltage power lines are significant sources of conducted EMI.
How EMI Noise Affects Devices
EMI noise doesn’t just cause minor annoyances; it can have significant impacts on the functionality and longevity of your devices. Here’s how:
- Performance Degradation:
- Reduced Data Speeds: EMI can slow down internet connections by disrupting Wi-Fi signals.
- Audio Distortion: Speakers and headphones may produce crackling or humming sounds.
- Device Malfunctions:
- Screen Flickering: Displays can flicker or go blank due to interference.
- Random Shutdowns: Sensitive electronics may shut down unexpectedly when exposed to strong EMI.
- Increased Error Rates:
- Data Corruption: EMI can cause errors in data transmission, leading to corrupted files or lost information.
- Communication Failures: Wireless communication devices may experience dropped calls or failed connections.
- Hardware Damage:
- Component Stress: Prolonged exposure to EMI can stress electronic components, shortening their lifespan.
- Overheating: Interference can cause devices to overwork, leading to overheating and potential damage.
Real-World Example:
Imagine you’re working on an important project using your laptop, and suddenly the screen flickers, and the system crashes. Upon investigation, you discover that a nearby cordless phone was emitting EMI noise, disrupting your laptop’s operations. By stopping the EMI noise—perhaps by moving the phone or using shielded cables—you can restore your device’s performance and prevent future interruptions.
Identifying EMI Noise in Your Environment
Before you can stop EMI noise, you need to identify its presence and pinpoint its source. Here are some strategies and tools to help you detect EMI noise:
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Unusual Device Behavior: Unexpected shutdowns, slow performance, or erratic functioning.
- Audible Interference: Humming, buzzing, or crackling sounds from speakers or headphones.
- Visual Disturbances: Flickering screens, inconsistent lighting, or display anomalies.
- Tools and Methods for Detection:
- EMI Detectors and Analyzers:
- Handheld EMI Meters: Portable devices that can detect and measure electromagnetic interference levels.
- Spectrum Analyzers: More advanced tools that provide a detailed analysis of the frequency spectrum to identify specific sources of EMI.
- Software Solutions:
- Diagnostic Software: Some applications can monitor device performance and detect anomalies that may indicate EMI noise.
- Visual Inspection:
- Cable Checks: Look for damaged or poorly shielded cables that might be conducting EMI.
- Device Placement: Assess the positioning of electronic devices to identify potential sources of interference.
- EMI Detectors and Analyzers:
- Step-by-Step Identification Process:
- Observe the Symptoms: Note when and where the interference occurs.
- Isolate Devices: Turn off or unplug devices one by one to identify the source.
- Use Detection Tools: Employ EMI detectors or spectrum analyzers for precise identification.
- Document Findings: Keep a record of sources and their impact to effectively address the issues.
Pro Tip:
Sometimes, EMI noise can be sneaky, hiding behind the scenes. If you’re experiencing unexplained device issues, consider relocating your electronics to different areas or rearranging your workspace to see if the interference diminishes. A little detective work can go a long way in stopping EMI noise!
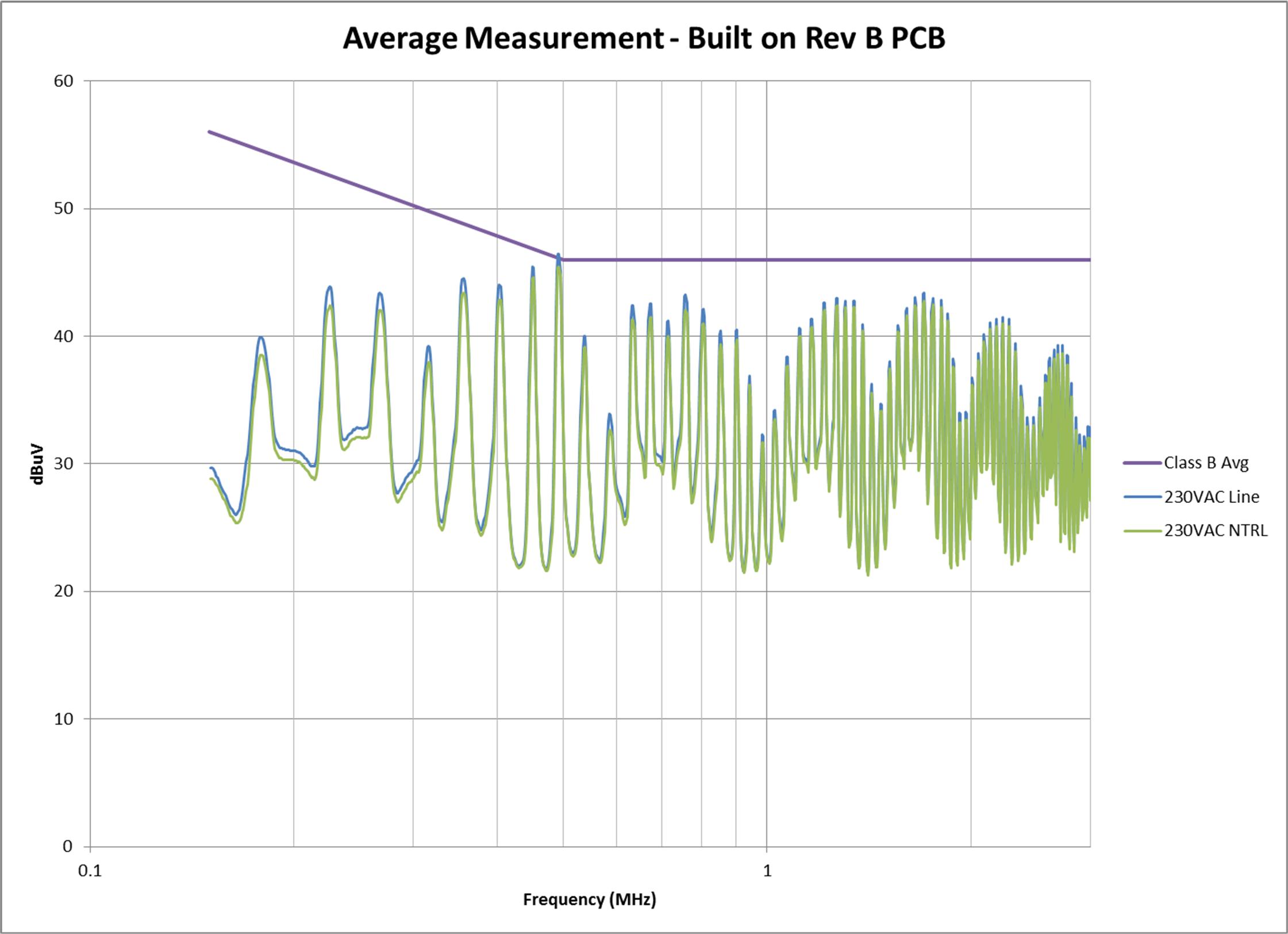
Causes of EMI Noise
Now that you have a solid understanding of what EMI noise is and how it affects your devices, it’s time to delve into the why—the various causes of EMI noise. Identifying the root causes is essential for effectively stopping EMI noise and preventing it from wreaking havoc on your electronic environment.
Electrical Wiring and Infrastructure
Electrical wiring and infrastructure are often the unsung heroes—or villains—when it comes to EMI noise. Poorly designed or outdated electrical systems can be a breeding ground for electromagnetic interference, leading to a myriad of device issues. Here’s how:
Poorly Shielded Cables
Imagine trying to have a private conversation in a room full of chatterboxes. That’s essentially what happens with poorly shielded cables. When cables lack adequate shielding, they become susceptible to EMI noise, allowing unwanted electromagnetic waves to seep in and disrupt signal transmission.
- Types of Shielding:
- Foil Shielding: Offers excellent protection against high-frequency interference.
- Braided Shielding: Provides good coverage and flexibility, ideal for environments with physical stress.
- Spiral Shielding: Balances flexibility and protection, suitable for devices that require frequent movement.
Solution: Upgrading to high-quality, shielded cables can significantly reduce EMI noise. Ensure that cables are properly grounded and routed away from potential interference sources.
Grounding Issues
A solid grounding system is the backbone of any electrical infrastructure. Grounding issues, such as improper connections or insufficient grounding, can create loops that act like antennas, picking up and amplifying EMI noise.
- Common Grounding Problems:
- Floating Grounds: When a device’s ground is not connected to a common reference point.
- Ground Loops: Multiple ground paths causing circulating currents that generate interference.
- Corroded Connections: Poor connections leading to inconsistent grounding.
Solution: Conduct a grounding audit to ensure all devices are properly grounded. Use single-point grounding techniques to eliminate ground loops and maintain a clean electrical environment.
Faulty or Aging Equipment
Faulty or aging equipment is another major source of EMI noise. As electronic devices age, their components can degrade, leading to increased susceptibility to interference and even generating their own EMI.
Worn-Out Components
Over time, components such as capacitors, resistors, and inductors can wear out, compromising their ability to filter out EMI noise effectively.
- Signs of Worn-Out Components:
- Frequent Device Failures: Regular malfunctions or shutdowns.
- Inconsistent Performance: Fluctuating device behavior without apparent cause.
- Increased Heat Generation: Overheating components due to inefficient operation.
Solution: Regularly inspect and maintain your equipment. Replace worn-out components promptly to restore optimal performance and minimize EMI noise.
Improper Maintenance
Neglecting proper maintenance can exacerbate EMI issues. Dust accumulation, loose connections, and outdated firmware can all contribute to increased electromagnetic interference.
- Maintenance Neglect Indicators:
- Dust-Covered Equipment: Reduces cooling efficiency and can cause overheating.
- Loose Connections: Create intermittent contact points, leading to signal disruptions.
- Outdated Firmware: May lack the latest EMI mitigation features.
Solution: Implement a routine maintenance schedule to keep your equipment clean, connections secure, and firmware up to date. Regular maintenance helps in preventing EMI noise before it becomes a significant problem.
External Sources of EMI
Sometimes, the source of EMI noise isn’t within your immediate environment but comes from external factors. These external sources can be particularly challenging to control but understanding them is crucial for effective mitigation.
Nearby Radio Towers
Radio towers emit powerful electromagnetic waves to broadcast signals over long distances. While necessary for communication, these towers can be a significant source of EMI noise, especially if they are in close proximity to your devices.
- Impact of Radio Towers:
- Signal Overlap: Interferes with your wireless devices’ frequencies.
- Persistent Interference: Continuous emission can lead to chronic device issues.
Solution: Utilize frequency filtering techniques and shielded enclosures to protect your devices from external radio frequency interference. In some cases, relocating sensitive equipment further away from the tower can help reduce exposure.
Power Lines
High-voltage power lines are notorious for generating conducted EMI noise. The vast amount of electrical energy flowing through these lines can induce interference in nearby electronic systems.
- Effects of Power Line EMI:
- Noise on Data Lines: Causes disruptions in internet and communication cables.
- Increased Electrical Noise: Affects the overall electrical environment of a building.
Solution: Install EMI filters on power lines and use shielded cabling for data transmission. Additionally, maintaining a proper distance between power lines and sensitive equipment can help mitigate interference.
Wireless Signals and Devices
In our wirelessly connected world, devices like smartphones, tablets, and smart home gadgets are everywhere. While convenient, these wireless signals and devices are prime contributors to EMI noise.
Overlapping Frequencies
With multiple devices operating on similar frequency bands, overlapping signals can lead to interference and EMI noise. For example, Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, and cordless phones often share the 2.4 GHz band, causing signal congestion and interference.
- Common Overlapping Frequencies:
- 2.4 GHz Band: Used by Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and some cordless phones.
- 5 GHz Band: Primarily for Wi-Fi, but can also experience congestion in dense environments.
Solution: Switching to less congested frequency bands (e.g., moving from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz) can alleviate interference. Additionally, using dual-band routers and frequency hopping techniques can help distribute the load more evenly across available bands.
Signal Congestion
In environments with a high density of wireless devices, signal congestion becomes a significant issue. The sheer number of devices competing for bandwidth can lead to increased EMI noise and degraded performance.
- Consequences of Signal Congestion:
- Reduced Data Throughput: Slower internet speeds and laggy connections.
- Increased Latency: Delays in data transmission affecting real-time applications like gaming and video conferencing.
Solution: Optimizing wireless network settings and limiting the number of active devices can help reduce congestion. Implementing mesh networks or wired connections where possible can also alleviate the strain on wireless frequencies.
Common Causes of EMI Noise
| Cause | Description | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Poorly Shielded Cables | Inadequate shielding allows EMI to interfere | Upgrade to shielded cables, proper grounding |
| Grounding Issues | Improper grounding creates interference loops | Conduct grounding audit, single-point grounding |
| Worn-Out Components | Degraded components fail to filter EMI effectively | Regular maintenance, replace faulty components |
| Improper Maintenance | Neglected equipment leads to increased EMI | Implement routine maintenance schedules |
| Nearby Radio Towers | External radio emissions causing interference | Use frequency filtering, shielded enclosures |
| Power Lines | High-voltage lines induce conducted EMI noise | Install EMI filters, use shielded data cables |
| Overlapping Frequencies | Multiple devices on similar bands causing interference | Switch frequency bands, use dual-band routers |
| Signal Congestion | High density of wireless devices leading to EMI noise | Optimize network settings, use mesh or wired setups |
Real-World Case Study: EMI Noise in a Smart Home
Scenario: Meet Jane, a tech-savvy homeowner who recently upgraded her house to a smart home with various interconnected devices—smart lights, thermostats, security cameras, and more. Shortly after the upgrade, Jane noticed intermittent connectivity issues, slow response times, and occasional device malfunctions.
Investigation: Upon closer inspection, Jane discovered that her Wi-Fi router was struggling to handle the sheer number of connected devices, all operating on the same 2.4 GHz frequency band. Additionally, her older smart bulbs lacked proper shielding, contributing to EMI noise that interfered with other devices.
Solution: Jane decided to upgrade her router to a dual-band model, enabling better distribution of devices across 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. She also replaced the poorly shielded smart bulbs with newer, EMI-compliant models. Finally, Jane organized her wireless devices to minimize overlapping frequencies and implemented mesh networking to ensure a more stable and interference-free connection.
Outcome: The combination of these strategies effectively stopped the EMI noise, resulting in a seamless smart home experience with reliable device performance and enhanced network stability.
Pro Tip:
Understanding the causes of EMI noise is half the battle in stopping EMI noise. By addressing issues related to electrical wiring, equipment maintenance, and wireless device management, you can create a more harmonious electronic environment. Remember, a little proactive maintenance and thoughtful device placement can go a long way in minimizing electromagnetic interference!
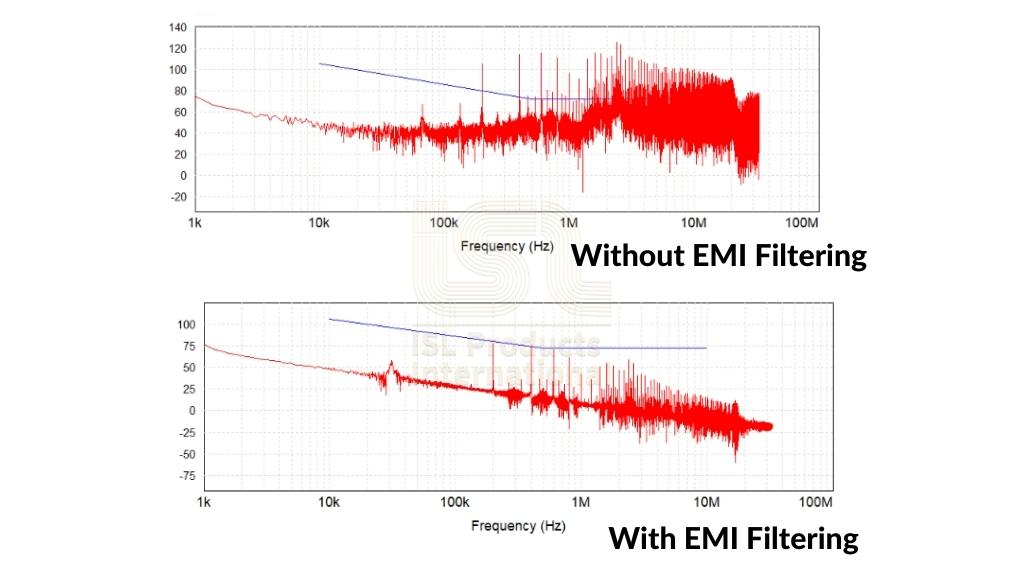
How to Stop EMI Noise: Step-by-Step Solutions
Now that you’ve uncovered the causes of EMI noise, it’s time to roll up your sleeves and dive into the solutions. From identifying the pesky sources to implementing effective mitigation strategies, we’ve got you covered. Let’s embark on this journey to silence the interference!
Identifying the Source of EMI Noise
Before you can stop EMI noise, you need to identify its source. Think of it as being a detective in your own electronic mystery. Here’s how to pinpoint the culprit:
- Conducting a Thorough Inspection
- Visual Inspection: Start by examining all your electronic devices and their connections. Look for damaged cables, loose connections, or signs of wear and tear.
- Device Isolation: Turn off or unplug devices one at a time to see if the EMI noise dissipates. This helps in narrowing down the source.
- Using EMI Detectors and Analyzers
- Handheld EMI Meters: These portable devices can detect and measure electromagnetic interference levels in your environment. They’re user-friendly and perfect for quick checks.
- Spectrum Analyzers: For a more detailed analysis, spectrum analyzers provide a comprehensive view of the frequency spectrum, helping you identify specific interference sources.
- Software Solutions
- Diagnostic Software: Some applications can monitor your device’s performance and alert you to anomalies that may indicate EMI noise. Examples include Wi-Fi analyzers and system performance monitors.
- Documenting Findings
- Keep a Log: Maintain a record of when and where the interference occurs. Note the devices in use during these times to help identify patterns.
Pro Tip:
Sometimes, the source of EMI noise is hiding in plain sight. If you’re struggling to find the culprit, try rearranging your workspace or relocating devices to different areas to see if the interference levels change. A fresh perspective can often reveal hidden sources of EMI.
Improving Shielding and Grounding
Once you’ve identified the source, it’s time to shield your devices and ensure proper grounding to stop EMI noise effectively.
- Types of Shielding Materials
- Foil Shielding: Offers excellent protection against high-frequency interference. It’s thin and flexible, making it ideal for sensitive components.
- Braided Shielding: Provides good coverage and flexibility. It’s durable and suitable for environments where cables are subject to physical stress.
- Spiral Shielding: Balances flexibility and protection. It’s perfect for devices that require frequent movement, such as laptops and mobile chargers.
- Proper Grounding Techniques
- Single-Point Grounding: Ensures that all devices are connected to a common ground point, eliminating ground loops that can cause interference.
- Grounding Audit: Regularly check all grounding connections to ensure they are secure and corrosion-free. Replace any faulty grounding components immediately.
- Implementing Shielded Enclosures
- Shielded Cases: For particularly sensitive equipment, consider using shielded enclosures that block external electromagnetic fields.
- Shielded Rooms: In industrial settings, EMI-safe rooms can be constructed to house critical equipment, providing a controlled environment free from interference.
Fun Fact:
Did you know that the first EMI shielded cables were developed in the early 20th century to prevent interference in telegraph systems? Technology has come a long way since then, but the principles remain the same!
Upgrading or Replacing Faulty Components
Faulty or aging components can be a significant source of EMI noise. Upgrading or replacing these parts is essential to stop EMI noise and ensure your devices function optimally.
- Signs of Faulty Equipment
- Frequent Failures: Devices that regularly malfunction or shut down unexpectedly are likely suffering from internal EMI issues.
- Inconsistent Performance: If a device’s performance fluctuates without any apparent reason, it might be struggling with internal interference.
- Increased Heat Generation: Overheating components can indicate that the device is working harder to combat EMI noise, leading to potential damage.
- Best Practices for Replacement
- Choose High-Quality Components: Invest in certified, high-quality parts that are designed to handle EMI noise effectively.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always adhere to the installation and maintenance instructions provided by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine checks and maintenance to identify and replace faulty components before they escalate into bigger issues.
Real-World Example:
Consider a small business owner, Tom, who noticed his office computers were crashing frequently. After a thorough inspection, he discovered that his old power supplies were the culprits, emitting excessive EMI noise. By upgrading to high-quality, EMI-compliant power supplies, Tom not only stopped the EMI noise but also enhanced the overall performance of his office equipment.
Managing Wireless Interference
In our wirelessly connected world, managing wireless interference is crucial to stop EMI noise and maintain seamless device performance.
- Optimizing Device Placement
- Distance Matters: Keep wireless devices away from each other to reduce the chances of interference. For example, place your Wi-Fi router away from cordless phones and Bluetooth devices.
- Height and Orientation: Position devices at optimal heights and orientations to minimize signal overlap and enhance coverage.
- Changing Channel Frequencies
- Wi-Fi Channels: Switch your Wi-Fi router to a less congested channel. Tools like Wi-Fi analyzers can help identify the best channels with minimal interference.
- Bluetooth Channels: Similarly, adjusting the channels used by Bluetooth devices can reduce overlapping frequencies and minimize interference.
- Implementing Dual-Band Routers
- 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz: Dual-band routers operate on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, allowing devices to spread out their connections and reduce congestion.
- Smart Channel Selection: Some modern routers automatically select the best available channel, ensuring optimal performance with minimal interference.
- Frequency Hopping Techniques
- Adaptive Frequency Hopping (AFH): This technology allows devices to rapidly switch frequencies to avoid interference, ensuring a more stable connection.
- Spread Spectrum Technology: Distributes the signal over a wide range of frequencies, making it less susceptible to interference and enhancing overall reliability.
Pro Tip:
If you’re experiencing persistent wireless interference, consider using wired connections where possible. Ethernet cables provide a stable, interference-free connection, freeing up your wireless bandwidth for devices that truly need it.
Using Ferrite Beads and Filters
Ferrite beads and EMI filters are effective tools to stop EMI noise by absorbing and blocking unwanted electromagnetic interference.
- How Ferrite Beads Work
- Magnetic Absorption: Ferrite beads are made from magnetic materials that absorb high-frequency noise, preventing it from traveling along cables.
- Installation: Simply clip or snap ferrite beads onto cables near the source of interference. They are easy to install and inexpensive.
- Installing EMI Filters on Cables
- Power Line Filters: These filters block EMI noise from entering or leaving power lines, ensuring a clean power supply to your devices.
- Data Line Filters: Used on USB, Ethernet, and other data cables, these filters prevent EMI from disrupting data transmission.
- Choosing the Right Filters
- Frequency Range: Ensure the filters you choose are designed to block the specific frequencies causing interference.
- Type of Connection: Select filters that are compatible with your cable types and connectors for seamless integration.
Fun Fact:
Ferrite beads were originally developed for radio technology to prevent interference in communication systems. Today, they’re a staple in virtually every electronic device, silently working to stop EMI noise.
Maintaining Proper Cable Management
Proper cable management is not just about aesthetics; it plays a crucial role in preventing and stopping EMI noise by reducing the chances of cable-induced interference.
- Organizing and Separating Cables
- Avoid Crossing Cables: Keep power cables separate from data cables to minimize the risk of conducted EMI noise.
- Bundle Cables Neatly: Use cable ties or Velcro straps to bundle cables together, reducing clutter and preventing entanglement that can lead to interference.
- Using Shielded Cables
- Choose Shielded Varieties: Opt for shielded USB, Ethernet, and HDMI cables that are designed to block EMI noise.
- Double-Shielding: In environments with high EMI levels, consider double-shielded cables for added protection.
- Implementing Cable Trays and Conduits
- Cable Trays: Use cable trays to organize and support cables, keeping them off the floor and away from sources of interference.
- Conduits: Protect cables from external EMI by running them through shielded conduits.
- Labeling Cables
- Easy Identification: Labeling cables helps in quickly identifying and isolating problematic cables during troubleshooting.
- Efficient Maintenance: Clear labels make cable management more efficient, reducing the time spent on maintenance and upgrades.
Real-World Example:
Sarah, a graphic designer, faced frequent Wi-Fi drops while working on tight deadlines. After implementing proper cable management—separating her power cables from data lines and using shielded Ethernet cables—she noticed a significant reduction in EMI noise, leading to a more stable and productive workspace.
Implementing Surge Protectors and Power Conditioners
Surge protectors and power conditioners are essential for stopping EMI noise by regulating the power supply and protecting your devices from electrical disturbances.
- Benefits of Surge Protection
- Protects Against Voltage Spikes: Shields your devices from sudden power surges that can cause EMI noise and hardware damage.
- Enhances Device Longevity: By providing a stable power supply, surge protectors help extend the lifespan of your electronics.
- Choosing the Right Power Conditioner
- Noise Filtering: Look for power conditioners that offer EMI and RFI filtering to block unwanted interference from the power lines.
- Voltage Regulation: Ensures a consistent voltage level, preventing fluctuations that can contribute to EMI noise.
- Capacity: Select a power conditioner with adequate wattage and outlets to support all your connected devices.
- Installation Tips
- Central Location: Place surge protectors and power conditioners in a central location where they can effectively manage the power supply to multiple devices.
- Avoid Daisy-Chaining: Do not connect multiple surge protectors in series, as this can overload the system and reduce effectiveness.
- Maintenance and Replacement
- Regular Inspections: Periodically check surge protectors for signs of wear or damage. Replace them if they show any physical damage or if they no longer provide adequate protection.
- Indicator Lights: Many surge protectors come with indicator lights that show whether they are functioning correctly. Ensure these lights are always green and steady.
Fun Fact:
The first surge protector was invented in the 1920s to protect radios from voltage spikes. Today, they’re indispensable for safeguarding a wide range of electronic devices against EMI noise and other electrical disturbances.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Stop EMI Noise
| Solution | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Identifying the Source | Use inspection, detectors, and software to find EMI sources | Accurate targeting of interference |
| Improving Shielding and Grounding | Upgrade shielding materials and ensure proper grounding | Reduces and blocks EMI noise |
| Upgrading Faulty Components | Replace worn-out parts with high-quality, EMI-compliant ones | Enhances device performance and longevity |
| Managing Wireless Interference | Optimize device placement and switch frequency bands | Minimizes wireless EMI noise |
| Using Ferrite Beads and Filters | Install ferrite beads and EMI filters on cables | Absorbs and blocks unwanted electromagnetic interference |
| Maintaining Proper Cable Management | Organize and shield cables to prevent interference | Reduces cable-induced EMI noise |
| Implementing Surge Protectors | Use surge protectors and power conditioners to regulate power | Protects devices and ensures a stable power supply |
Real-World Case Study: Stopping EMI Noise in a Home Office
Scenario: Mike, a freelance video editor, set up a home office equipped with multiple monitors, a high-powered computer, and various peripherals. Soon after, he began experiencing screen flickering, audio dropouts, and intermittent internet connections—classic signs of EMI noise.
Investigation: Mike started by identifying the source of EMI noise. He noticed that his old, unshielded Ethernet cables and a nearby cordless phone were the main culprits. Additionally, his power strips lacked surge protection, allowing EMI to seep into his devices.
Solutions Implemented:
- Upgraded to shielded Ethernet cables and repositioned his cordless phone away from the computer.
- Installed ferrite beads on all cables to absorb high-frequency interference.
- Reorganized his cable setup to separate power lines from data cables, reducing the chances of conducted EMI.
- Added a power conditioner with EMI filtering to ensure a stable and clean power supply to all his equipment.
Outcome: After implementing these solutions, Mike experienced a drastic reduction in EMI noise. His screens no longer flickered, audio quality improved, and his internet connection became stable. The enhanced setup not only stopped the EMI noise but also boosted his overall productivity.
Pro Tip:
When tackling EMI noise, start with the simplest solutions and gradually move to more complex ones if needed. Sometimes, rearranging your devices or upgrading a single cable can make a significant difference. Remember, consistency and patience are key to effectively stopping EMI noise and maintaining a harmonious electronic environment!